
(Sören Kierkegaard)
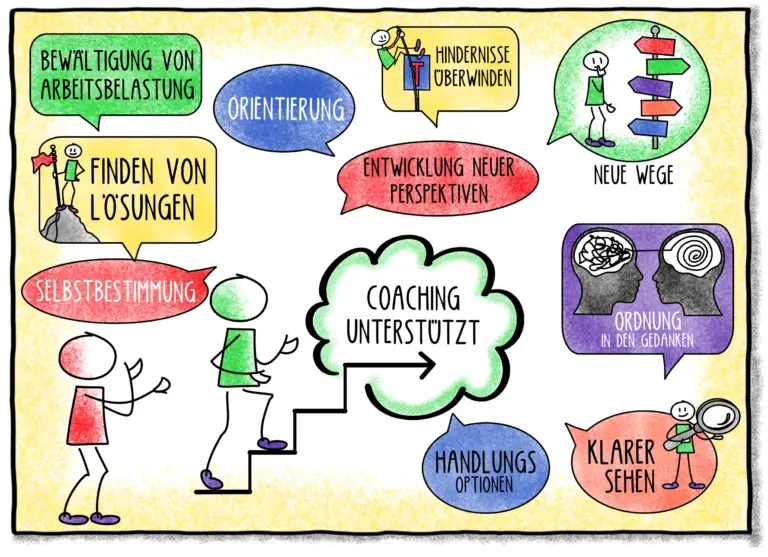


At the beginning of each coaching session, coach and coachee get to know each other and clarify the coachee’s expectations with the coach’s possibilities. An important basis is the relationship of trust that makes effective cooperation possible in the first place.
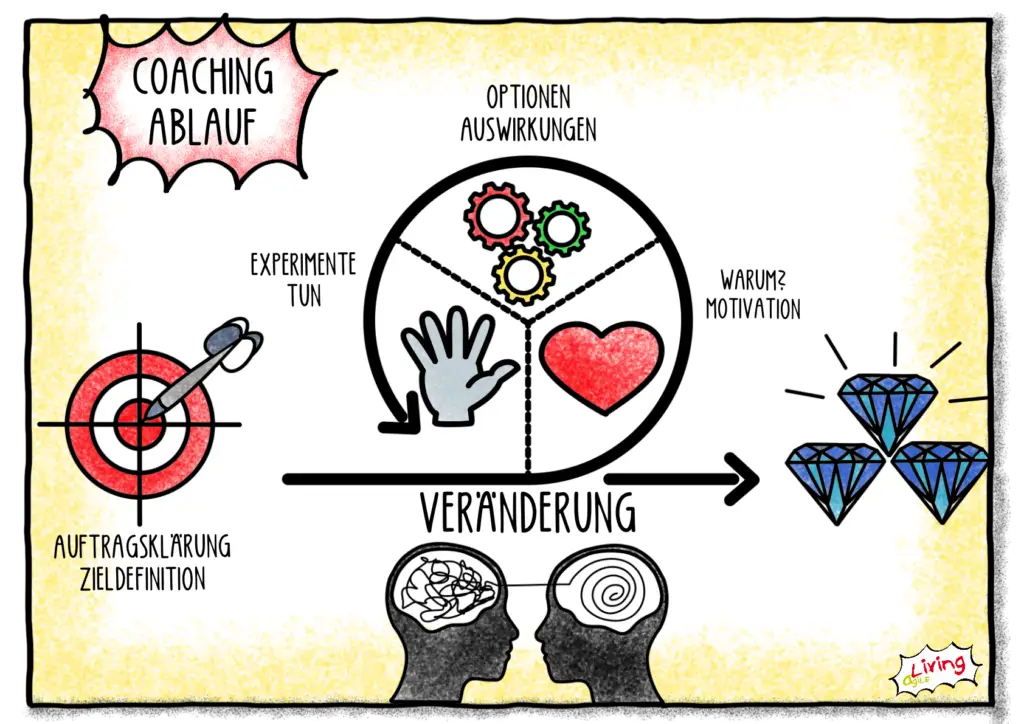
In a contract, the organisational framework conditions such as frequency, duration, costs and development goals are jointly defined and recorded in writing.
The following questions can serve as a guide to the content:
In this phase, the client’s goals and problems are worked on. Using appropriate coaching methods, options for action are developed and first concrete steps are prepared. The experiences with these steps are discussed in the next session.
At the end of each session there is time for a review and an outlook into the next period.
At the end of the coaching process, when the problems have been worked through, solutions found and goals achieved, it is time to say goodbye.
After the coaching, the time of learning and change begins. In this phase it is possible to arrange small telephone sessions for support.
However, the next coaching phase should not take place for a few months. This serves to avoid psychological dependence.
copyright agile-living ©2021
+49 179 5122527